The four smart community projects funded by the Japanese government, in collaboration with the private sector, included various residential demand response schemes. These demonstration experiments conducted from FY2011 – FY2015 have shown peak reduction levels of 10% to 20%by relying on a combination of technologies eg, Home Energy Management Systems (HEMS) as well as time-of-use (TOU) or critical-peak pricing (CPP) for residential electricity users. Based on these preliminary results, researchers led by Kyoto University’s Professor Ida, have conducted cost-benefit simulations to evaluate the impact of expansion of residential demand response (DR) across all of Japan (excluding Okinawa). The goal of the study was to evaluate the cost and benefits of residential demand response based on universal adoption of HEMS, as proposed by Japan’s Cabinet Secretariat in 2012.
To download the full presentation in pdf, click here.
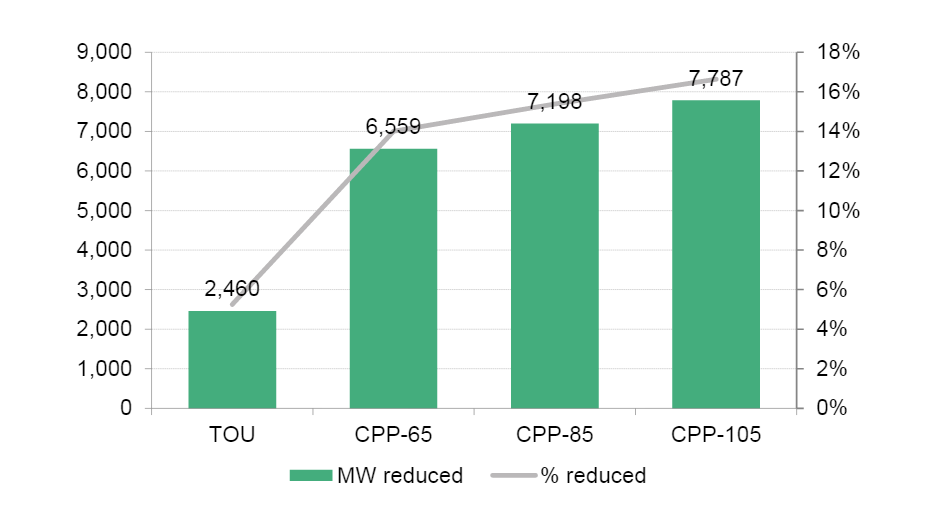
Figure: Peak demand reduction by each DR retail menu (left axis: MW, right axis: %)
Source: Kyoto University Research Team