By Isshu Kikuma, Senior Associate, Energy Storage, BloombergNEF
- Global energy storage capacity additions to grow 23% in 2025
- China and US to remain two largest markets through 2035
Global energy storage additions are on track to set another record in 2025 with the two largest markets – China and US – overcoming adverse policy shifts and tariff turmoil. Annual deployments are also set to scale in Germany, the UK, Australia, Canada, Saudi Arabia and Sub-Saharan Africa, driven by supportive policies, procurement by utilities and power market dynamics.
Another all-time high energy storage installation
Globally, annual energy storage deployment (excluding pumped hydropower plants) is set to hit another all-time high at 92 gigawatts (247 gigawatt-hours) in 2025 – 23% higher than in 2024. China accounts for over 50% of the annual build in gigawatts, followed by the US at 14%. Energy storage additions in these two markets remain strong for now although recent policy changes slow new solar and wind in both markets.
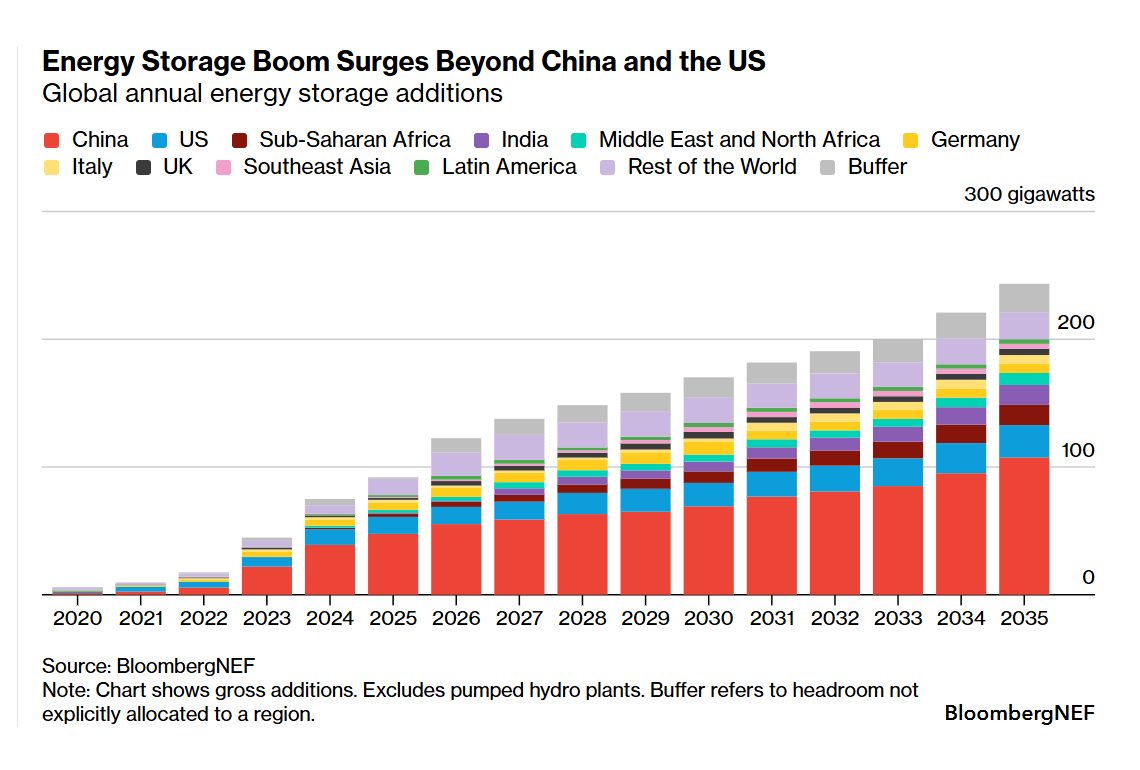
Energy storage installations globally will keep gaining momentum over the next decade as other markets pick up pace. BloombergNEF expects cumulative energy storage capacity in 2035 to reach 2 terawatts (7.3 terawatt-hours) – eight times the level in 2025. Utility-scale projects continue to dominate applications.
See 2H 2025 Energy Storage Market Outlook for more details.
China and the US shake off policy headwinds
Despite policy headwinds earlier in the year, energy storage additions in China and the US are set to continue growing this decade.
The removal of storage mandates in China for renewables and the absence of offsetting drivers were big concerns. However, a new energy storage target was set in September, underlining the commitment of the world’s second largest economy to the sector. China also aims to accelerate the shift from mandates to market-driven growth through the spot market launch and the provincial compensation scheme.
In the US, federal policy shifts brought uncertainty due to frequent changes in import tariffs and new restrictions on the use of equipment from China. Still, market players are quickly adapting to the new environment, supported by domestic battery manufacturing initiatives by leading Korean firms. With slower-than-expected battery demand for electric vehicles, battery makers are shifting focus to stationary energy storage.
Lithium-ion battery storage duration is extending beyond four hours
Lithium iron phosphate (LFP) remains the prevalent lithium-ion battery chemistry in the stationary energy storage market largely due to its cost advantage and higher cycle life compared to nickel-based lithium-ion battery chemistry.
Lithium-ion battery storage duration is also extending to six to eight hours, enabling it to compete against other novel long-duration energy storage technologies. These six- to eight-hour projects – often procured through schemes targeting longer-duration energy storage – are being planned in many markets such as the UK, Australia, Canada, Japan South Korea and Italy.
BloombergNEF clients can access the full report here.





